Aerospace engineer KR Sridhar always dreamed big: He used to work with NASA on technology to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen to support life on other planets or let humans breathe air on Mars. But as the Soviet Union fell and the space race slowed, Sridhar pivoted to providing clean energy technology for the rising global middle class.
He cofounded Ion America in 2001—renamed Bloom Energy five years later—with a focus on fuel cells that deliver cleaner, on-site, off-grid power. Fast forward to today’s AI race, and Bloom’s products just so happen to mesh with the needs of the data center boom that’s starving for massive power generation growth very quickly.
Fuel cells can hypothetically bring power online for data centers in months, not years, because they do not have to wait for the backlog of gas-fired turbines or the long queue for grid interconnections.
Bloom’s stock price has spiked 1,000% in 12 months—its market cap is now about $28 billion, up from $2.5 billion a year ago. The company has signed big data center deals with Oracle, American Electric Power (AEP), Equinix, and Brookfield Asset Management, the latter of which is a $5 billion partnership announced Oct. 13 to power AI factories globally, including Europe.
Bloom CEO Sridhar actually had data centers in mind as a big opportunity when he first pitched the company at the turn of the century. But the massive growth didn’t take off until after the ChatGPT launch.
“That’s when we said, ‘Everything that we’ve been telling the world is going to happen is now going to accelerate,’” Sridhar told Fortune.
“It’s a 24-year journey for an overnight success,” Sridhar said with a laugh. “I’m glad it’s in my lifetime.”
Renewable wind and solar energy still have some intermittency issues, even with batteries. And a sufficient supply of gas-fired and nuclear power stations are several years away, he said. That’s why on-site fuel cells are the answer, he says, both as a bridge and as a permanent power solution.
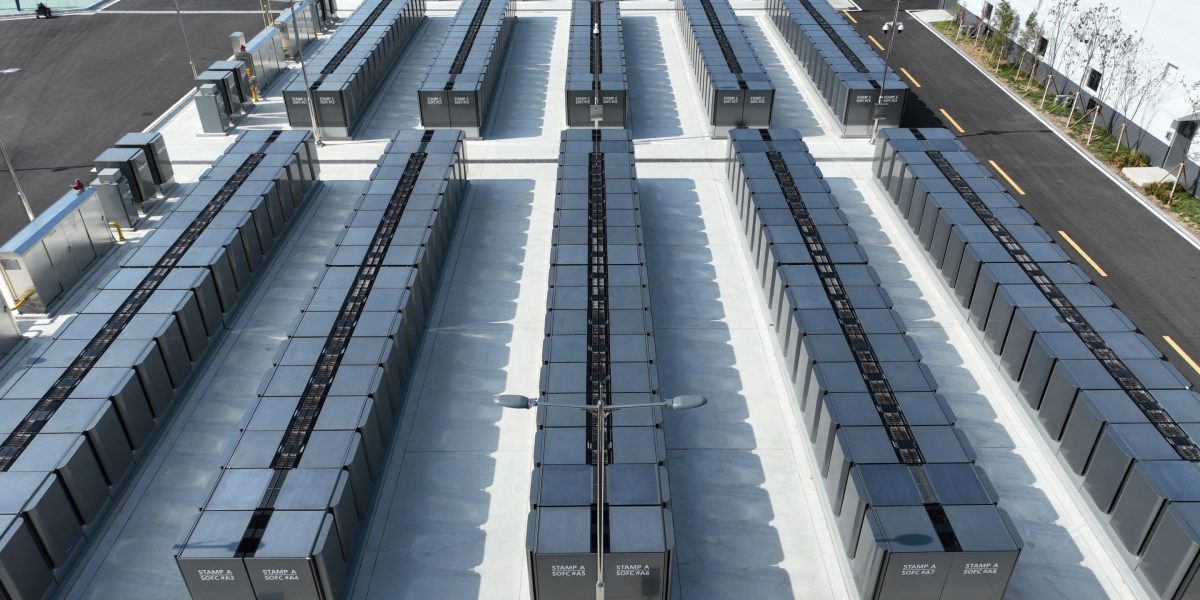
The company’s solid oxide fuel cells are a mature technology that have been developed over two decades. Thus far, Bloom has deployed 1.5 gigawatts of fuel cells—enough to power 1.2 million homes—with demand mounting by the day. The goal is to deploy 10 gigawatts per year from its manufacturing hubs in Fremont, California, and Newark, Delaware.
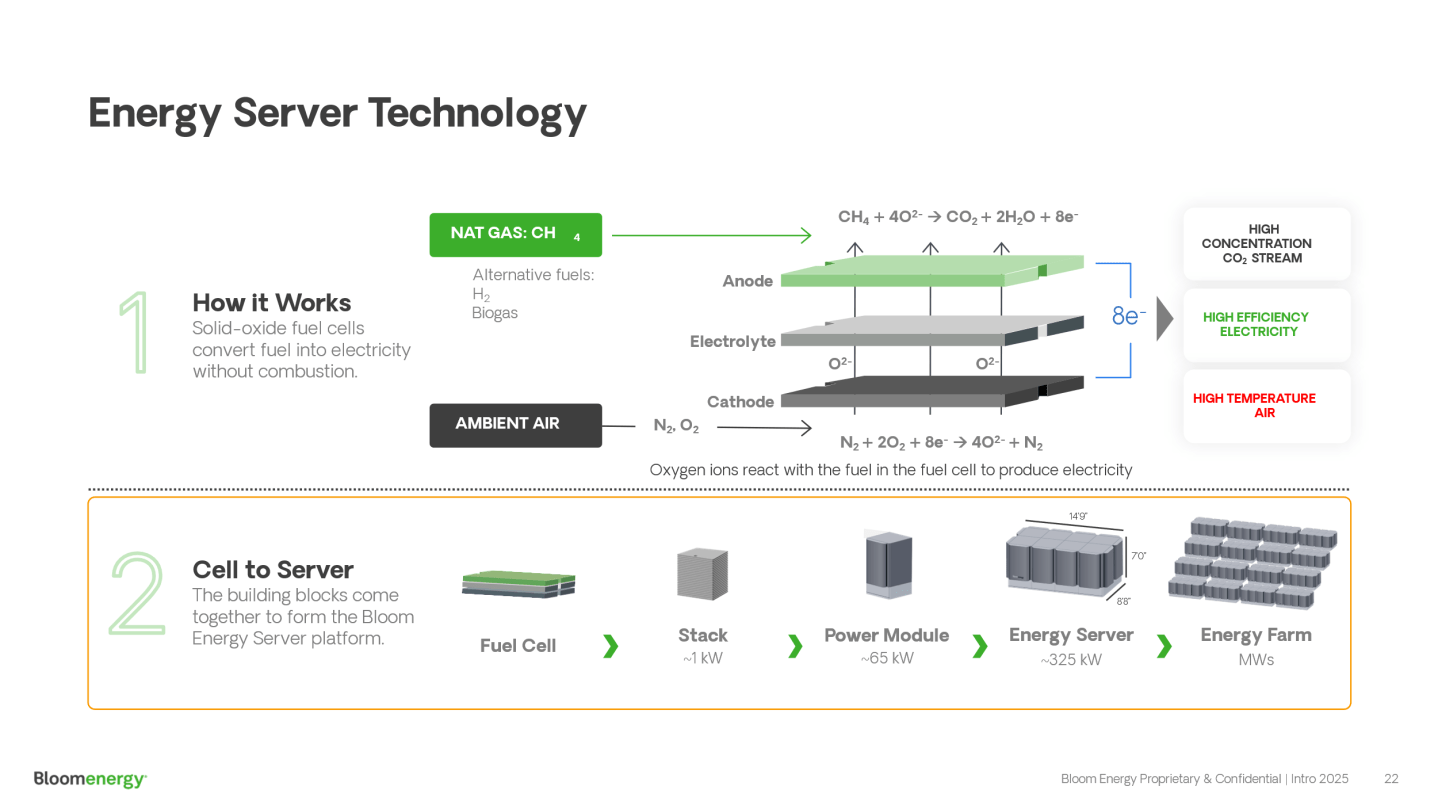
Fuel cells have existed for years, but they’ve lacked mainstream adoption because of their high manufacturing costs. They require expensive precious metals, corrosive acids, or hard-to-contain molten materials. Bloom’s solid oxide fuel cells use lower-cost ceramics—no precious metals—and they provide much greater electrical efficiency, operating at temperatures above 800 degrees Celsius.
The cells convert natural gas, hydrogen, or biogas into electricity through a clean electro-chemical process rather than dirty combustion. The cells are zero-carbon if they use green hydrogen, but they’re still cleaner than gas turbines even if they use natural gas. And the fuel cells are modular, so they can ramp up or down, or be relocated to other data centers when grid power becomes available.
Sridhar acknowledged the long journey to get here. Bloom took seven years to develop the first commercial cells. And then another decade to continually bring the costs down and improve their efficiency. In the meantime, Bloom relied on “early adopter” Fortune 100 customers who were willing to pay extra to power for cleaner power, including Google, Walmart, eBay, and FedEx.
From unicorn to large-cap stock
For years, Bloom was hyped as a Silicon Valley unicorn, but in 2012 the SEC charged an investment bank working with Bloom of using inflated numbers to mislead investors. Bloom was not accused of wrongdoing, and the company eventually went public in 2018.
The technology works more affordably now since fuel cell microgrids qualify for tax credits from President Trump’s One Big Beautiful Bill, said Marina Domingues, head of U.S. new energies research for the Rystad Energy research firm. She said they are comparable to the price of power from combined-cycle gas turbines, but fuel cells can come online more quickly and produce power more cleanly.
“Deta centers come with two main wish list requests. One of them is the power must be truly reliable,” she said. “Another one, which is probably the toughest, is that they need power now,” Domingues said. “They’re offering a solution exactly at the same time developers need it. There’s a lot of potential market growth for a company like Bloom.”
Pushing a fuel cell imperative
Much of the AI boom’s focus is on massive hyperscaler campuses in rural areas, such as OpenAI’s Stargate project in Abilene, Texas, and beyond. But Sridhar insists fuel cells will not only be helpful, they’ll become imperative once the race is on to build more and more smaller data centers in increasingly urban areas closer to consumer demand.
“The only two raw materials [that AI needs] are data and electricity,” Sridhar said. “It’s extremely electricity intense. They have to produce their own power on site.
“You’re not going to have any choice but on-site power, because no city has the distribution network that can accommodate those kinds of big [electricity] loads,” Sridhar said, citing Memphis, Tennessee, as an example of public outcry amid rising emissions for powering data centers. “If it’s in your backyard or outside your office window, you want it to be clean.”
Elham Akhavan, Wood Mackenzie senior microgrid research analyst, said Bloom’s competitors—including FuelCell Energy, Doosan Group’s HyAxiom, and Plug Power—offer different variations on the technology but they have not yet scaled up as much as Bloom.
As the technology advanced, the fuel cell sector was able to reposition itself from being a mere provider of backup power to a primary power source—with the grid as the backup, she said.
“Bloom led fuel cell deployment across North America way before data center demand arrived,” Akhavan said. “It’s a prime power solution in a very small footprint, and rest of the land is available for the data centers.”
Domingues said Bloom has a multitude of factors working to its advantage, including a head start on competitors, a domestic manufacturing chain when Trump is pushing onshoring and tariffs, and an early bet on fuel cells for “stationary power” when many potential rivals focused on fuel cells for the transportation sector.
“Bloom bet on the stationary power path, and they also had strong relationships with some of the traditional data center market,” Domingues said. “That allows them some competitive advantages against their peers.”
The company is currently unprofitable. Bloom operated at a $29 million net loss in 2024, improved from a roughly $300 million loss in 2023. But Bloom also lost $66 million in the first half of 2025.
Sridhar insists the lack of profitability will be short lived. “We are not one of these companies that has to invest, invest, invest. We’ve already done that part the last 20 years. We have the flywheel spinning already. Accelerating is going to take less and less energy.”
Sridhar said Bloom intentionally built its manufacturing plants as exact copies so they can continue to scale up more quickly to match demand and offer rapid returns on investment. “We believe the market demand is going to be there because electricity abundance is what’s going to generate a better quality of life and wealth in a digitized world,” he said.
Sridhar is still inspired by his dreams of Mars: “Living off the land is truly what an explorer does. So, I started producing oxygen, breathing air, water, electricity, heat on Mars so someday humans can live there,” he said. On Earth, “Clean energy is what we need on the planet in a very reliable way, everywhere, and with access.”


 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Business8 years ago
Business8 years ago
 Tech8 years ago
Tech8 years ago