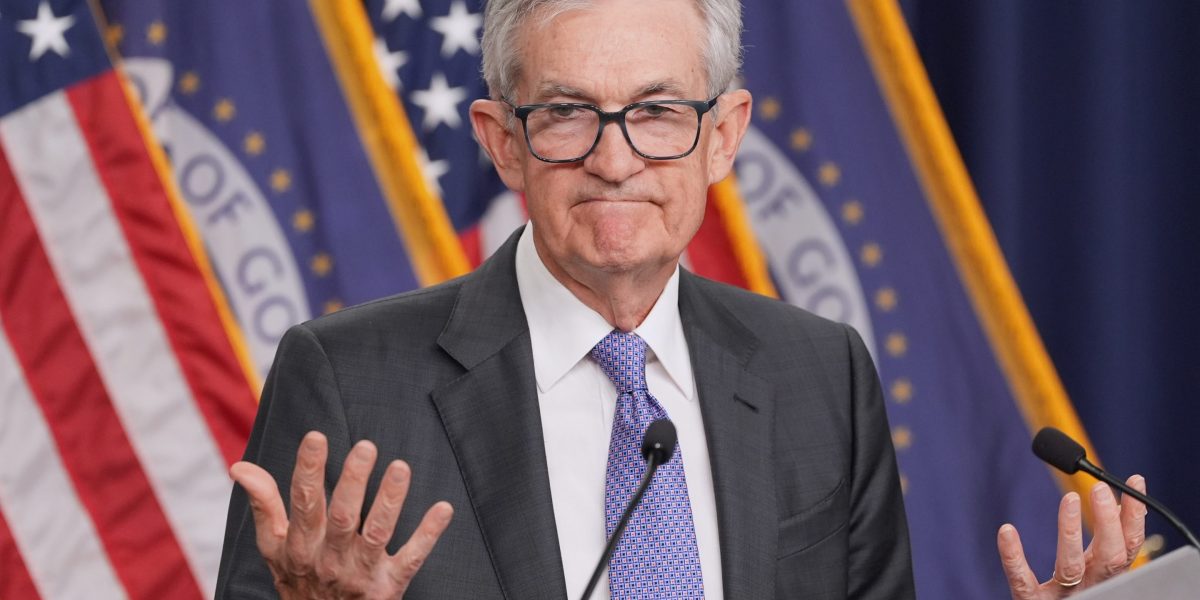
As the Trump administration ramps up its pressure campaign against the central bank — now including Justice Department subpoenas and the threat of criminal charges — Senate Republicans have closed ranks around Powell, defending an independent Fed chair under attack from a president of their own party.
“I know Chairman Powell very well. I will be stunned — I will be shocked — if he has done anything wrong,” said GOP Sen. John Kennedy of Louisiana, one of Trump’s most reliable allies in the Senate.
Soon after the Justice Department served subpoenas on the Fed, Powell went on the offensive, releasing a video statement accusing the administration of using “pretexts” to pressure the central bank into sharply cutting interest rates, as Trump has demanded. The 72-year-old Fed chair also leaned on Capitol Hill relationships he has cultivated since his 2018 appointment, holding multiple calls with Republican senators in the days following the video’s release.
“He knows his way around Congress,” said Robert Tetlow, a former senior policy adviser at the Fed. “He gets in there, pets the dog, shoots the breeze, and has a way of getting people to like him, and he’s really good at it.”
For some in Congress, it’s personal
In a March 2024 hearing, Powell received an unusual greeting from a member of the Senate Banking Committee: The office dog had said hello.
“Gus sends his regards,” said Sen. Thom Tillis, a North Carolina Republican. “If you have time after the hearing, you ought to go by and see him.”
“I don’t want to disturb his nap,” Powell said to laughter in the hearing room.
Now, Tillis — who is retiring at the end of this year — has been among the Republicans rushing to Powell’s defense, vowing to withhold support for any Trump administration nominees to the Federal Reserve until the legal cloud surrounding the chair is resolved.
Alaska Sen. Lisa Murkowski put her support behind Tillis’ plan to block nominees. She was among the multiple Republican senators who said they spoke with Powell after his video statement.
“I look at the situation with Jay Powell and this supposed investigation of the overhaul of their offices going over there as grounds to do nothing but intimidate, threaten and coerce,” Murkowski told reporters. Powell goes by “Jay” informally.
Murkowski and Tillis have not shied away from critiquing the Trump administration in recent months. What makes the Powell backlash unique is that even reliable Trump allies — and opponents of the Fed’s recent decisions — have rushed to the Fed chair’s side.
“I believe strongly in an independent Federal Reserve,” said Pennsylvania Sen. Dave McCormick, who also sits on the Senate Banking Committee. The first-term senator added that he agrees “with President Trump that Chairman Powell has been slow to cut interest rates” but said he doesn’t “think Chairman Powell is guilty of criminal activity.”
Senate Majority Leader John Thune, R-S.D., said that the investigation “better be real” and “better be serious.”
In the House, Financial Services Chair French Hill criticized the Justice Department’s investigation.
“I know Mr. Powell to be a man of integrity with a strong commitment to public service,” he said. “While over the years we have had our policy disagreements, I found him to be forthright, candid, and a person of the highest integrity.”
Decades of service in Washington
Hill also said in his statement that he has “known Chairman Powell since we worked together at Treasury during the George H.W. Bush Administration.”
Powell, a Republican, has been a fixture in the nation’s capital for decades, where he developed a reputation as a centrist. He worked at the Bipartisan Policy Center, a think tank, from 2010 to 2012 and pushed congressional Republicans toward compromise during their budget battles with President Barack Obama.
Obama, in turn, appointed Powell to the Fed’s governing board in 2012. Trump then elevated him to the Chair position in 2018. He was reappointed by President Joe Biden in 2022.
Powell also built up credibility among Republicans in the House and Senate by largely ignoring Trump’s personal attacks during the president’s first term in office, when he complained about rate hikes by Powell in 2018. In general, Powell has tried to keep his head down and avoid a back-and-forth with the White House. A solid economy — at least until the COVID pandemic struck — also helped protect the Fed during Trump’s first term.
Powell has often cited support on Capitol Hill as a counterweight to Trump’s attacks. At a news conference last July, Powell discussed the importance of distancing the Fed from “direct political control,” because that allows the central bank to take unpopular steps such as raising interest rates to thwart inflation.
“I think that’s pretty widely understood,” he said. “Certainly, it is in Congress.”
Powell’s public schedule underscores his commitment to staying connected with Congress. In the month following Trump’s inauguration last year, he met with or spoke by phone with 27 senators from both parties, according to his schedule.
After testifying before the Senate Banking Committee about the renovation of Fed buildings in June of last year, Powell followed up with the chair, Tim Scott, and the ranking member, Democratic Sen. Elizabeth Warren, about the cost of the project.
“As is to be expected in the major renovation of nearly 100-year-old historic buildings, the Board’s designs have continued to evolve over the course of the project,” wrote Powell.
The accusations against Powell
The subpoenas served to the Fed relate to Powell’s comments about the $2.5 billion renovation of two office buildings, which Trump has criticized as excessive.
“The threat of criminal charges is a consequence of the Federal Reserve setting interest rates based on our best assessment of what will serve the public, rather than following the preferences of the President,” Powell said in a video statement.
Trump has insisted he was unaware of the investigation into Powell. When asked by CBS News whether the subpoenas were a form of retribution, Trump said Tuesday, “I can’t help what it looks like.”
Trump has gone after several officials he sees as having done him wrong, including an attempted firing of another Fed board member, Lisa Cook. The Supreme Court has allowed Cook to keep her job and will hold a hearing on her case on Wednesday.
But not all of Trump’s efforts are sticking, with federal inquiries against former FBI Director James Comey and New York Attorney General Letitia James tossed out by the courts.
“So far it looks like this has been a misstep for the administration,” said Lev Menand, a law professor at Columbia University and author of a book about the Fed. “This attempt to go after Jay Powell with a potential criminal indictment is leading to significant resistance from elected officials even within the Republican Party.”

 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics9 years ago
Politics9 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Entertainment9 years ago
Entertainment9 years ago
 Business9 years ago
Business9 years ago
 Tech8 years ago
Tech8 years ago