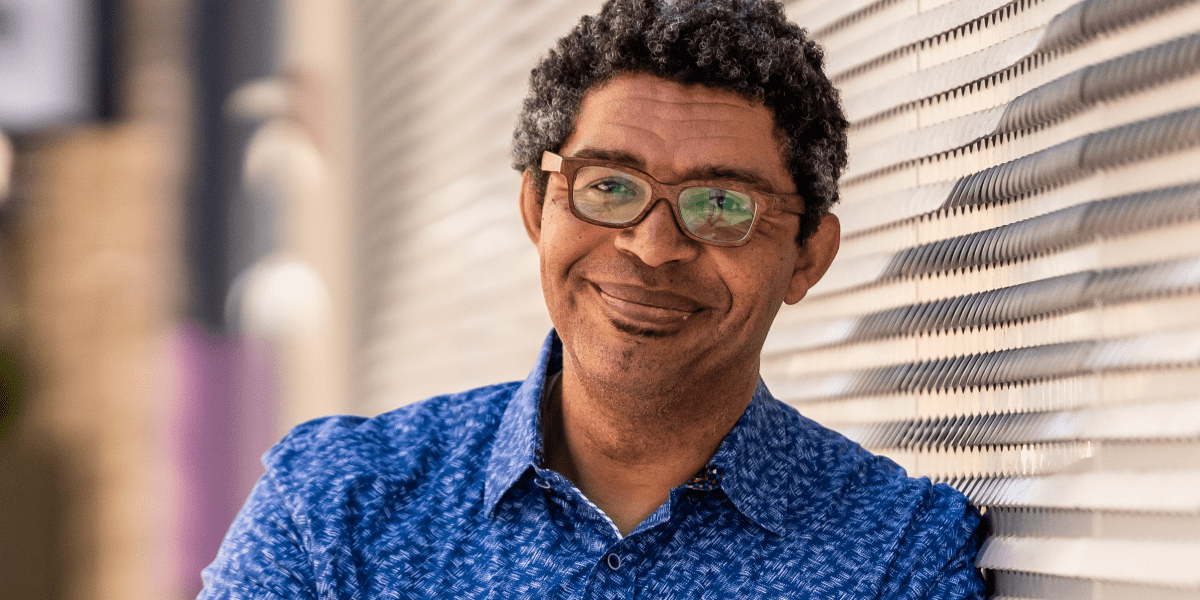
New York Assemblymember Alex Bores, a Democrat now running for Congress in Manhattan’s 12th District, argues that one of the most alarming uses of artificial intelligence—highly realistic deepfakes—is less an unsolvable crisis than a failure to deploy an existing fix.
“Can we nerd out about deep fakes? Because this is a solvable problem and one that that I think most people are missing the boat on,” Bores said on a recent episode of Bloomberg’s Odd Lots podcast, hosted by Joe Weisenthal and Tracy Alloway.
Rather than training people to spot visual glitches in fake images or audio, Bores said policymakers and the tech industry should lean on a well-established cryptographic approach similar to what made online banking possible in the 1990s. Back then, skeptics doubted consumers would ever trust financial transactions over the internet. The widespread adoption of HTTPS—using digital certificates to verify that a website is authentic—changed that.
“That was a solvable problem,” Bores said. “That basically same technique works for images, video, and for audio.”
Bores pointed to a “free open-source metadata standard” known as C2PA, short for the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, which allows creators and platforms to attach tamper-evident credentials to files. The standard can cryptographically record whether a piece of content was captured on a real device, generated by AI, and how it has been edited over time.
“The challenge is the creator has to attach it and so you need to get to a place where that is the default option,” Bores said.
In his view, the goal is a world where most legitimate media carries this kind of provenance data, and should “you see an image and it doesn’t have that cryptographic proof, you should be skeptical.”
Bores said thanks to the shift from HTTP to HTTPS, consumers now instinctively know to distrust a banking site that lacks a secure connection. “It’d be like going to your banking website and only loading HTTP, right? You would instantly be suspect, but you can still produce the images.”
AI has become a central political and economic issue, with deepfakes emerging as a particular concern for elections, financial fraud, and online harassment. Bores said some of the most damaging cases involve non-consensual sexual images, including those targeting school-age girls, where even a clearly labeled fake can have real-world consequences. He argued that state-level laws banning deepfake pornography, including in New York, now risk being constrained by a new federal push to preempt state AI rules.
Bores’s broader AI agenda has already drawn industry fire. He authored the Raise Act—a bill that aims to impose safety and reporting requirements on a small group of so-called “frontier” AI labs, including Meta, Google, OpenAI, Anthropic and XAI—which was just signed into law last Friday. The Raise Act requires those companies to publish safety plans, disclose “critical safety incidents,” and refrain from releasing models that fail their own internal tests.
The measure passed the New York State Assembly with bipartisan support, but has also triggered a backlash from a pro-AI super PAC, reportedly backed by prominent tech investors and executives, which has pledged millions of dollars to defeat Bores in the 2026 primary.
Bores, who previously worked as a data scientist and federal-civilian business lead at Palantir, says his position isn’t anti-industry but rather an attempt to systematize protections that large AI labs have already endorsed in voluntary commitments with the White House and at international AI summits. He said compliance with the Raise Act, for a company like Google or Meta, would amount to hiring “one extra full-time employee.”
On Odd Lots, Bores said cryptographic content authentication should anchor any policy response to deepfakes. But he also stressed that technical labels are only one piece of the puzzle. Laws that explicitly ban harmful uses—such as deepfake child sexual abuse material—are still vital, he said, particularly while Congress has yet to enact comprehensive federal standards.
“AI is already embedded in [voters’] lives,” Bores said, pointing to examples like AI toys aimed at children to bots mimicking human conversation.
You can watch the full Odd Lots interview with Bores below:
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
Source link


 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Business8 years ago
Business8 years ago
 Tech8 years ago
Tech8 years ago