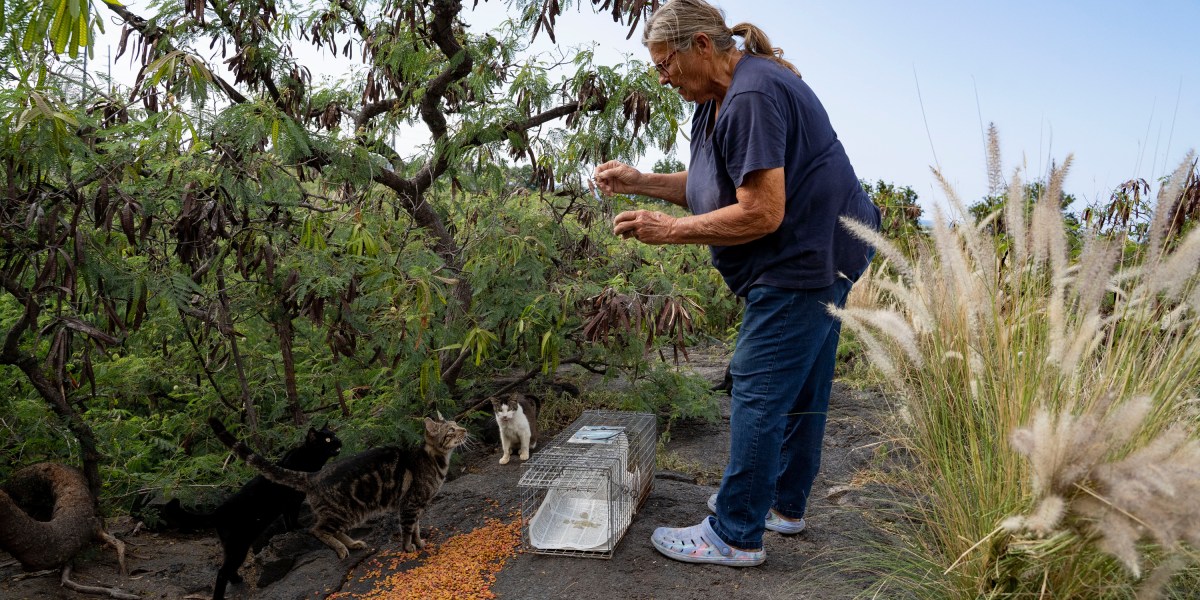
Throngs of feral cats emerge from the shade of parked trucks and bushes as soon as the familiar Subaru Forester pulls into a dump on Hawaii’s Big Island. They run after the vehicle to a certain meal — a gravy train that might not be around much longer.
A Hawaii County law set to take effect at the start of the new year bans feeding feral animals on county property. It’s an effort to protect native species, such as an endangered goose called the nene, from a super predator introduced to the islands by Europeans in the 18th century.
But the measure doesn’t sit well with many cat lovers, including the driver of the Subaru, Liz Swan, who has been feeding feral felines on the Big Island for 33 years.
“I don’t believe the cats should be exterminated at the expense of the nene,” Swan said. “They’re both living creatures.”
It’s unclear how many feral cats — abandoned pets and their descendants — live on the Big Island. Estimates range well into the tens of thousands, with pockets of dense colonies supported by people. Opponents of the ban say it will hamper their efforts to contain the population by trapping and neutering the animals — and that hungry cats will then have to hunt for food.
A variety of threats
About 200 cats live at the Kealakehe Transfer Station and Recycling Center, not far from the bustling tourist district of Kona. Swan shows up every late afternoon with water and kibble, and says she’s never seen a nene anywhere near the dump. Despite living amid trash, the cats there generally appear robust, most of them missing the tip of an ear, indicating they’ve been spayed or neutered.
The cats threaten the native species directly — by killing them — and indirectly, biologists say. Food left out for the cats can attract native animals, bringing them into closer contact with humans. Cat feces can also spread a parasite that causes toxoplasmosis, a disease that has killed endangered Hawaiian monk seals and native birds.
Last year, a male nene — pronounced “neh-neh” — was struck and killed by a car as it crossed a road in Hilo, on the eastern side of the island, to reach a cat feeding station. The goose’s surviving mate, which also had a gosling die of toxoplasmosis in 2024, has recently taken on another partner and is nesting in a Hilo park, the state Department of Land and Natural Resources announced this month.
The county’s feeding ban will help protect them, the department said.
A Hawaiian biologist’s view
State wildlife biologist Raymond McGuire recently checked for nene nesting sites among the barren black-rock fields near a shopping center at the Waikoloa resort. It’s not their traditional habitat, but he has seen the geese fly in to grab food — risking getting hit by cars — and last year some nested there.
As he approached, a pair of feline eyes peered out of a crack in the lava rock. Cats emerged from their nooks, perhaps mistaking him for someone who might offer food.
McGuire was relieved to see there were no nene nearby — but frustrated with evidence the cats are being fed: empty water bowls and aluminum pans.
He’s a cat owner — “my favorite animal is a cat” — but as a Hawaiian whose love of nature inspired him to pursue conservation work, he believes there is no room for them where native species are struggling to survive.
“There’s so many birds that my kids will never see, that I got to see,” he said, referring to native forest birds. “I think about my ancestors and I do wonder: Are we honoring them well in what we do? Because they did take steps to protect them.”
Feral cats are a problem in many places, but Hawaii’s sensitive ecosystem is full of species that evolved without mammalian predators, making them especially vulnerable, McGuire said.
‘I felt bad for the cats’
Hawaiian culture is closely tied to Hawaii’s animals; aumakua, or ancestral spirit guides, can take animal form, noted Big Island Mayor Kimo Alameda. His family’s aumakua is the shark, he said.
After the county council passed the measure with a veto-proof 6-2 vote, Alameda decided to let it take effect without his signature. Opponents persuaded him it would harm the cats.
“I had a soft spot for that,” he said. “I felt bad for the cats.”
The debate was so contentious that some opponents sent him hate messages, Alameda said.
The mayor said he hopes police consider enforcement a low priority. Violations carry fines of up to $50 for a first offense and up to $500 for subsequent offenses.
Will the ban prompt feeders to work in secret?
The answer is simple to Makaʻala Kaʻaumoana, a cultural practitioner — someone who works to preserve Hawaiian cultural traditions — on the island of Kauai.
Trapping, neutering and releasing cats makes no difference because they can still hunt, she said.
“The cats have to be removed,” she said.
Debbie Cravatta, who feeds cats in her West Hawaii neighborhood, questioned why.
“It’s a native species — why does that reign over a domestic cat that somebody dumped out pregnant and that had six kittens out in the wild?” Cravatta said. “Why is that life more valuable than this life?”
Opponents also argue the ban might only push feeding efforts underground.
“I’m not going to let them starve,” Swan said.
___
Kelleher reported from Honolulu.


 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Politics8 years ago
Politics8 years ago
 Entertainment8 years ago
Entertainment8 years ago
 Business8 years ago
Business8 years ago
 Tech8 years ago
Tech8 years ago